How to protect your email from interception?
14-03-2022, 14:24
Tor browser: change your IP for free, bypass restrictions on access to your favorite websites, be completely anonymous and encrypt all transmitted information
Today I installed Tor on my Mac OS X for a test and everything works fine for me. If Tor does not work for you, then later in the article there are detailed instructions on how to configure Tor if the provider blocks access to it.
But it is best to use paid VPN services, I wrote about this in detail in this article. So everything works quickly and there are no problems. And Tor has always been very slow. Many, by the way, now advise you to access Tor via VPN, but the point is that if you have a VPN, then you don't need Tor. In this article, I talk in detail about what Tor is and how to use it.
In previous articles, we figured out how to hide information about the websites you visited from your colleagues and relatives, as well as how to hide your IP address from the administration of the website you visited. For these purposes, we suggested using your browser in private mode or completely clearing your browsing history, as well as using anonymizers, proxy servers and VPN services.
If you started reading our section "Anonymity on the Internet” from this place and do not know what an anonymizer, proxy server or VPN is, then do not be afraid of these terrible words, since you can figure out what it is by spending 15 minutes reading the relevant articles, and in the article "How to hide visited websites from colleagues and relatives?” you will learn how to configure your browser for private browsing.
All the methods described above did not provide complete anonymity, as they did not protect us from the "all-seeing eye" of your system administrator or Internet provider. So how can we become completely anonymous and encrypt all the transmitted information so that even experienced hackers cannot "listen" to us? How do I change my IP address to another country's address? How to get around bans on access to your favorite sites?
The distributed Tor network will help us solve these problems.
What is the Tor distribution network?
Tor (The Onion Router) is an officially free and open source program used to anonymize traffic. With the help of Tor software, a huge international network has been created from the computers of users of this network. When you visit a website using the Tor network, the data transmitted by your computer to the Internet will not only be securely encrypted, which will save them from being intercepted and read, but your computer will also access not directly to the required site, but through a long network of other computers, which will practically it is impossible to track which website you visited and what you did there. i.e. The Tor network will reliably protect you not only from spying on visitors to a particular website, but also hide all your online activity from prying eyes and ensure almost complete anonymity. And due to the fact that your computer accesses the required website not directly, but through other computers, this will allow you to bypass the "blacklist" of websites compiled by your system administrator or Internet service provider.
How does Tor work?
Let's take a concrete example. Let's say your system administrator has banned access to your favorite website at work www.facebook.com . To access this website, you don't even have to install Tor on your work computer. You install Tor on your flash drive at home, and at work run the Tor program from this flash drive and enter the website address in the browser that opens from the flash drive, configured for anonymity www.facebook.com . The data you transmit (in this case, the address of the website www.facebook.com) will be encrypted and transmitted to the first computer in the Tor network, then the data in the same encrypted form will be transmitted to computer 2 and further along the chain until the last computer in the chain transmits your request to the website www.facebook.com . Unfortunately, the website www.facebook.com does not support the public keys of the Tor network (if this were the case, the entire Internet would be anonymous), so data from the last computer in the chain to the website www.facebook.com they will go unencrypted. Data interception is possible on the last section of the chain, but it is difficult to implement in practice. The following picture clearly shows the scheme of the Tor network:
When using the Tor network, you can be sure of the following:
your sysadmin or Internet service provider administrator will not be able to find out which websites you visit, because instead of the website you are interested in, your computer will formally access one of the computers on the Tor network with some obscure domain name. In addition, with each new connection to Tor, the first computer of the Tor network will always be different;
the website you visit will record only the IP address of the last node of the chain in its logs, i.e. it will be almost impossible to find out your IP address;
your sysadmin, Internet service provider administrator or hacker connected to your computer will not be able to find out what information you are transmitting, since all data is encrypted;
if your sysadmin has blocked access to the website you are interested in, you can easily bypass this restriction, since in fact your computer will not access the website you are interested in, but the first computer on the Tor network that is assigned an incomprehensible domain name. In addition, every time you connect to the Tor network again, the first computer will always be different, so there is no point in denying access to it;
interception of unencrypted data is possible only at the last section when transferring data from the last computer of the Tor node to the website you want to visit. But in order to implement this practically, it is necessary to track the entire Tor chain, which is technically difficult to do, since there may be several dozen computers in it. And if you get access to a website that you have visited, it will still be impossible to understand who is who;
video on youtube.com you will not be able to watch, you will not be able to view PDF documents in the browser, as well as perform a number of other actions, since when working in anonymous mode, you have to disable all plugins in the browser that can be used to calculate your real IP address, namely: Java, Flash, ActiveX, RealPlayer, Quicktime, Adobe PDF and a number of others.
How does Tor differ from anonymizers and anonymous proxy servers?
data encryption. Tor encrypts data, but anonymizers and anonymous proxy servers do not. If you use an anonymizer or an anonymous proxy server, then your sysadmin, an Internet service provider administrator or a hacker who intercepted your data will easily be able to find out which websites you visited and which data (including usernames, passwords and bank card numbers) you transmitted. The Tor network encrypts all transmitted information, so if someone intercepts it, they will receive a meaningless set of bytes.;
anonymity. There is no guarantee that an anonymous proxy server does not transmit your IP address to the visited website. Without verification, it is impossible to be sure that an anonymous proxy server is really anonymous, and special technical knowledge and time are required for verification. Tor hides not only your IP address, but also the destination address (i.e. the addresses of the websites you visited);
the reliability of protecting your anonymity. When using an anonymizer or an anonymous proxy server, it is very easy to trace the chain, since the chain consists of only three computers (your computer, an anonymous proxy server, a remote computer with a website that you visited). Your anonymity depends on whether the anonymous proxy server stores and transmits information to third parties. When you use Tor, you trust information to at least several computers participating in the Tor network, selected completely randomly and located in different countries. Therefore, it will be extremely difficult to calculate you;
support for any TCP traffic. Anonymous proxy servers, as a rule, support only HTTP traffic (i.e. you will only be able to visit websites), and Tor can be configured to support almost any connection (FTP, HTTPS, POP/SMTP, ...);
free of charge. Using the Tor network is completely free, while no advertising is imposed on you, whereas in order to use the anonymizer, you will have to watch a lot of unnecessary advertising, and you will have to pay for using a full-fledged anonymous proxy server;
open source, excellent reputation. When we use an anonymizer or an anonymous proxy server, we do not know who the owner of the service is, what his motives are, whether he does not transmit information about users to everyone on demand, whether the service will disappear tomorrow. Tor has been known for a long time and has proven itself well. The source code of the Tor program is open, it is free and is in the public domain, anyone can check whether it transmits data to the special services;
low data transfer rate. Unfortunately, Tor is often slower than anonymizers and some proxy servers. You have to pay for complete anonymity. When connected to the Tor network, a chain of computers located around the world is built, but when the resulting chain turns out to be very slow, Tor makes it easy to change it to another one by simply pressing one button. Sometimes it helps well;
restricted access. Some websites block access from the anonymous Tor network.
Attention! Don't think that the distributed Tor network is 100% anonymous. No, you can still be calculated in various ways, for example, by decrypting traffic and tracing a chain of computers (you understand that this is very, very expensive and long, and it is unlikely that anyone will do this, unless, of course, you are an international terrorist), or by installing a keyboard spy on your computer, or by creating a Tor output server that will intercept your traffic.
Tor protects only those programs that work through it. If you have installed the Tor Browser package, but have not configured other programs to work through the Tor network, for example, other browsers, email clients (MS Outlook, The bat, ...), etc. network programs, then there can be no question of any anonymity. In short, after installing the Tor browser, only Internet surfing through Firefox configured for Tor will be anonymous, and if you use Opera, Safari, Chrome or Internet Explorer, surfing through these browsers will not be anonymous. It is best to use two browsers, for example, Tor Browser (configured for Firefox anonymity) for anonymous surfing and, for example, Google Chrome – for regular surfing on the Internet.
It is better not to use Tor when anonymity is not needed, for example, for online games, Internet radio or videos, for downloading large files, so as not to overload the network unnecessarily, and also not to commit illegal actions using the Tor network, for example, to send spam, harm websites, otherwise the owners different resources will have grounds to block access to the Tor network, and then the network may become useless.
Do not make the following mistakes when working with Tor:
do not use an email address registered anonymously during anonymous sessions. For anonymous sessions, use only a mailbox registered using Tor;
if you started blogging or using a website anonymously, don't forget to use Tor all the time to visit these resources;
do not forget to also anonymize traffic when working from someone else's computer, since the owner of this computer may come and ask who used it at such and such a time;
do not publish large texts of a similar style of writing under your usual name, because with the help of linguistic analysis it is easy to determine who the written text belongs to. If you write long texts on various topics during anonymous and non-anonymous sessions, then you can be calculated. In linguistic analysis, analysts check the average length of a sentence, dialogue, frequency of use of unique words, active vocabulary, statistics on the use of parts of speech, and much, much more.
Instructions for installing and using Tor and getting the IP address of the country you need
Tor Installation Guide
Download the Tor Browser package on the official website of the project: www.torproject.org . This package includes the Firefox browser configured by Tor developers to work anonymously. We do not recommend using other browsers or regular Firefox to work with Tor if you want to remain anonymous.
Attention! If you already have the Firefox browser installed, then first delete it.
so, open the Tor homepage www.torproject.org and follow the link "Download Tor”;
you will be taken to the Tor browser download page in different languages for different operating systems Tor Browser Downloads;
find and download the version of Tor in Russian in the table with available downloads. The Windows version is located in the first column, for Mac OS X – in the second, for Linux – in the third. If you have Windows, then you first need to determine whether a 32-bit or 64-bit version of Windows is installed on your computer, and download the appropriate version of the Tor browser. How to determine your version of Windows is written in this article on the Microsoft website: How to determine whether a 32-bit or 64-bit version of the Windows operating system is installed on your computer;
run the downloaded file (this is a self-extracting archive) and specify which directory to unpack Tor to. If you want to use Tor from a flash drive, specify the path to the flash drive;
after unpacking, the folder "Tor Browser" will appear in the folder you specified. Log in to this folder and run the "Start Tor Browser" file.
All Tor is installed, let's get to work!
Tor Usage Guide
after launching the "Start Tor Browser" file, you will see this window:
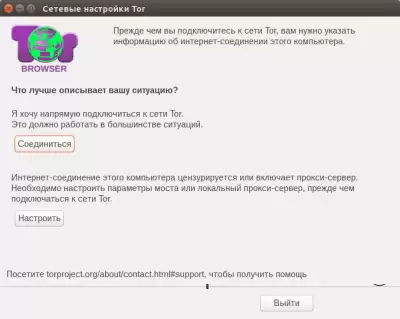 click the "Connect" button and you will see a Tor browser window (Firefox configured for Tor) in which you can use the Internet anonymously (see the picture below). Actually, that's all! Enter the addresses of the websites you need into the browser's address bar, open new tabs, use it like a regular browser.
click the "Connect" button and you will see a Tor browser window (Firefox configured for Tor) in which you can use the Internet anonymously (see the picture below). Actually, that's all! Enter the addresses of the websites you need into the browser's address bar, open new tabs, use it like a regular browser.
 What to do if your provider blocks access to the Tor network
What to do if your provider blocks access to the Tor network
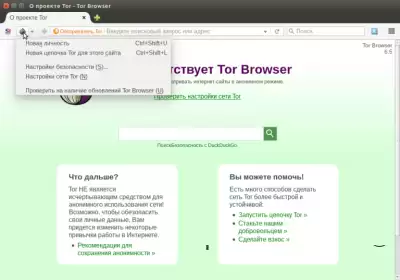
if you need to bypass the provider's ban on access to the Tor network, select the "Tor Network Settings" menu, as shown in the figure below:
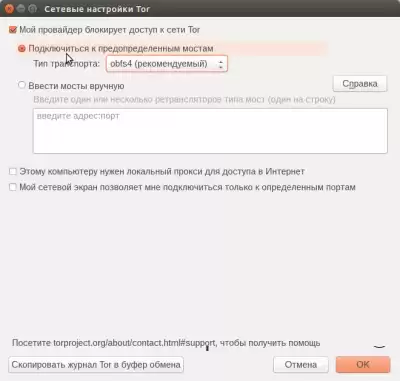
 and check the box “My provider has banned access to the Tor network” in the window that opens:
and check the box “My provider has banned access to the Tor network” in the window that opens:
The Tor Bridge Configuration window opens. Tor bridges are alternative entry points to the Tor network that are not publicly listed. Using a Tor bridge makes it more difficult, but not impossible for your ISP to know that you are using Tor. Select "Connect to Predefined Bridges" and click OK. If suddenly the browser does not start working, it means that the bridge used is already known to the provider, and you need to get a new bridge and enter it manually (see the picture below).
 How to get a Tor Bridge
How to get a Tor Bridge
Follow the link bridges.torproject.org and click the Step 2 Get bridges link. You will be taken to the page for getting bridges, where you need to click the green button “Just give me bridges!", enter a captcha and get bridges. To create a greater "masking" of the connection from the provider - in the "Advanced options" (see the picture below), select the type of repeater (obfs 2/3/4, scramblesuit or fte), and if you need repeaters with addresses from the IPv6 range, check the box "Yes!" and click the "Get bridges" button.
You can also get bridges by writing a letter to [email protected] with Gmail, Riseup, Yahoo. If you write from another service, the bridges will not be sent to you. In the text of the letter, insert the phrase "get bridges" (in Russian — get bridges). Almost immediately after sending the request, a message with the addresses of the nodes will be sent to the mailbox.
How to bypass the firewall (firewall)
if you need to bypass the firewall, select the "Tor Network Settings" menu, as shown in the figure below:
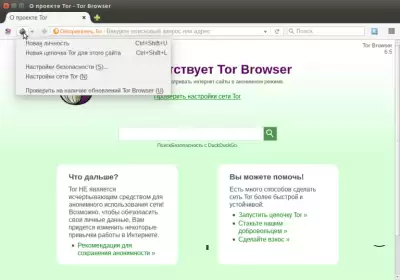 and check the box “My firewall allows me to connect to certain ports". After selecting this field, an additional field will appear in which you need to enter the allowed ports separated by commas.
and check the box “My firewall allows me to connect to certain ports". After selecting this field, an additional field will appear in which you need to enter the allowed ports separated by commas.
How to get the IP address of the country you need, or the choice of Tor exit nodes
If you want to get the IP address of the country you need at the output, then for this you need to enter the folder where you installed Tor (it is called "tor-browser_ru") and find the torrc configuration file in the folder: ...tor-browser_ru/Browser/TorBrowser/Data/Tor/. Open this file using the Notepad program and add a line to it:
ExitNodes $fingerprint,$fingerprint,…
Instead of $fingerprint, you need to enter the IP address of the node you need or the two-letter ISO code of the country you need in curly brackets, for example {de}, {ru}, {us}, etc. For example, if you need to have an American IP address, then you need this code:
ExitNodes {us}
You can specify comma-separated codes of different countries and/or IP addresses of nodes. A complete list of two-letter ISO codes of different countries can be found here: ISO 3166-1 alpha-2.
Unfortunately, the ExitNodes command does not work in strict mode, i.e. if a node belonging to the country you specified is not found, or if nodes from a given country turn out to be too slow, then Tor will use nodes from other countries. To avoid this, add one more line to the configuration file:
StrictExitNodes 1
In this case, if Tor does not find a single node in the right country, or the output node through which Tor connected to the website you need becomes unavailable, then Tor will stop working.
14-03-2022, 14:24
14-03-2022, 14:15
14-03-2022, 14:43


There are no comments
Information
Users of Visitor are not allowed to comment this publication.